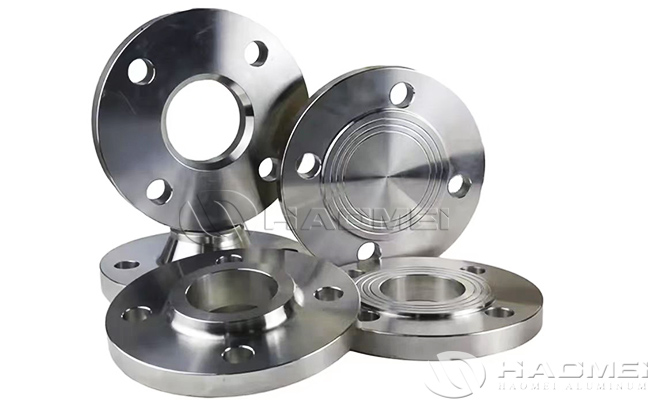
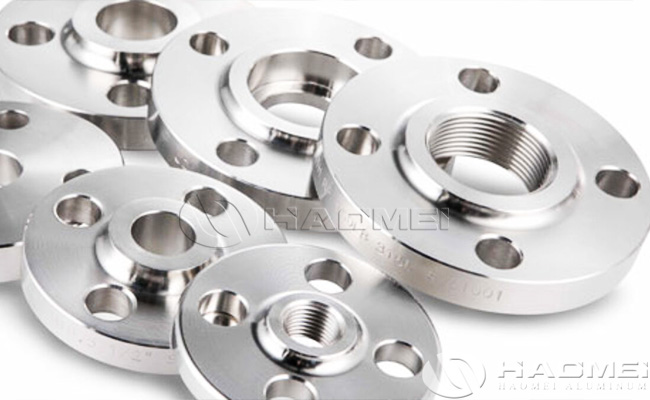
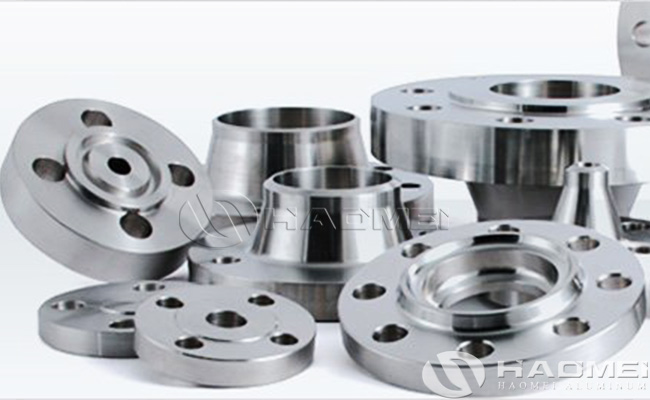
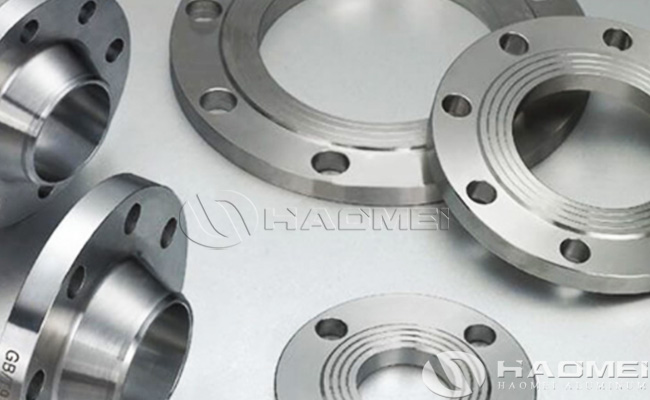
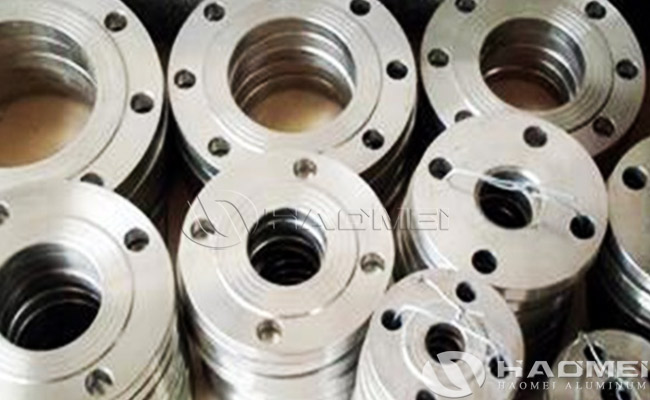
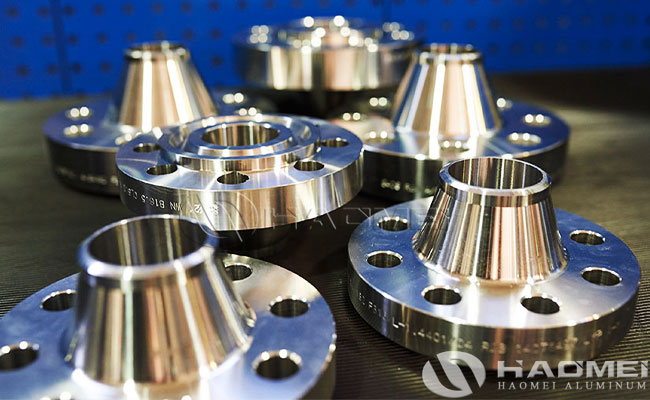
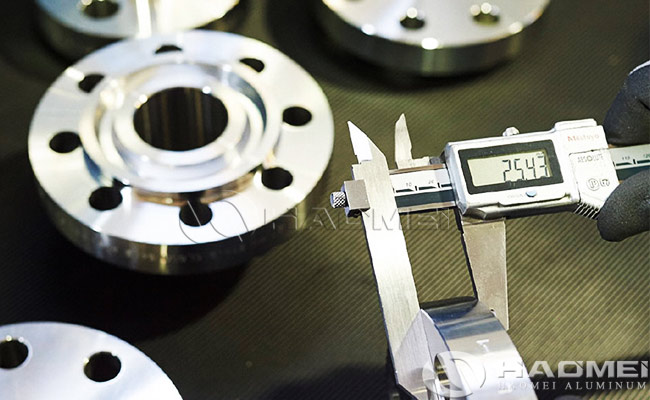
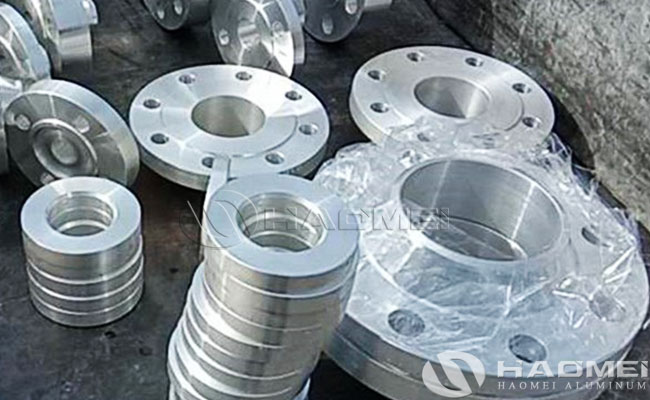
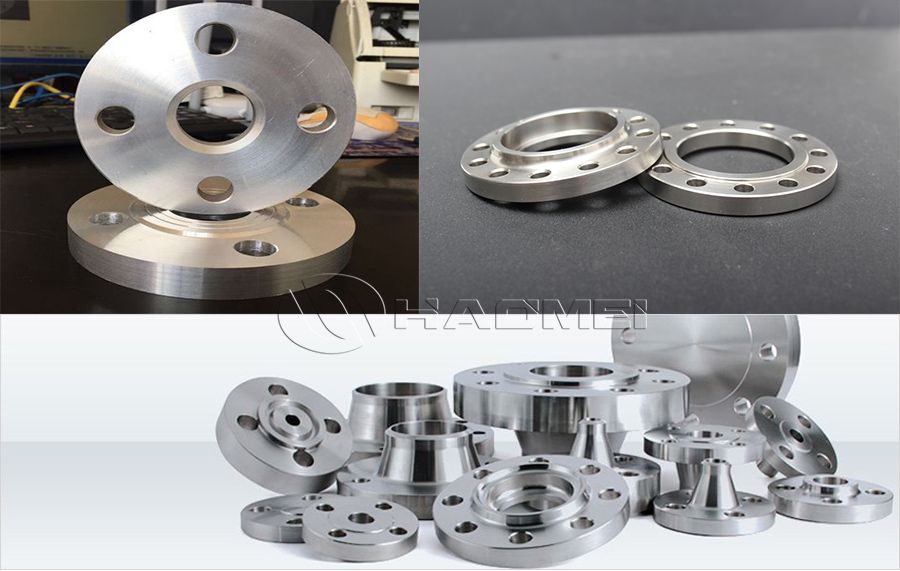
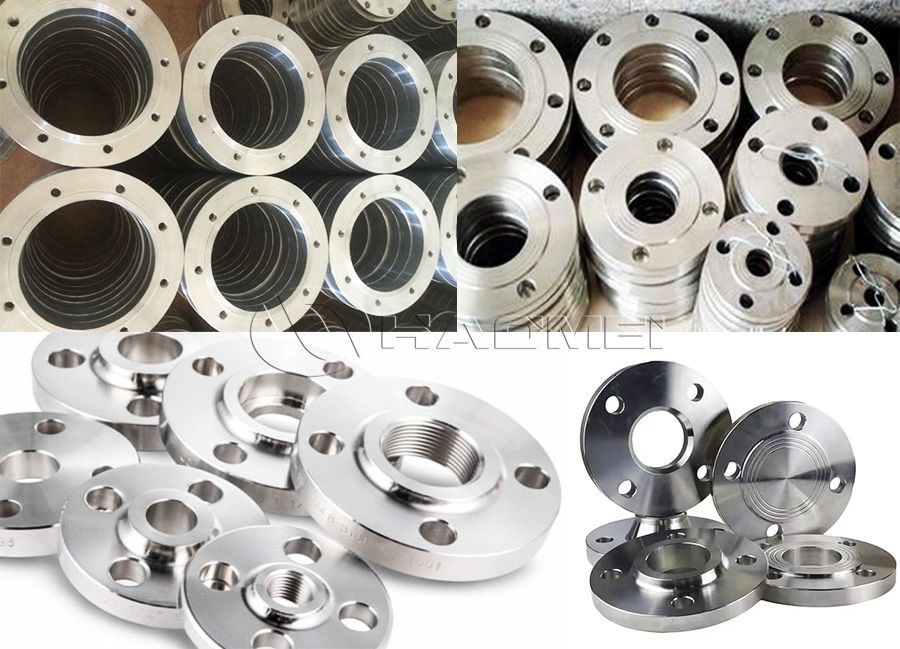
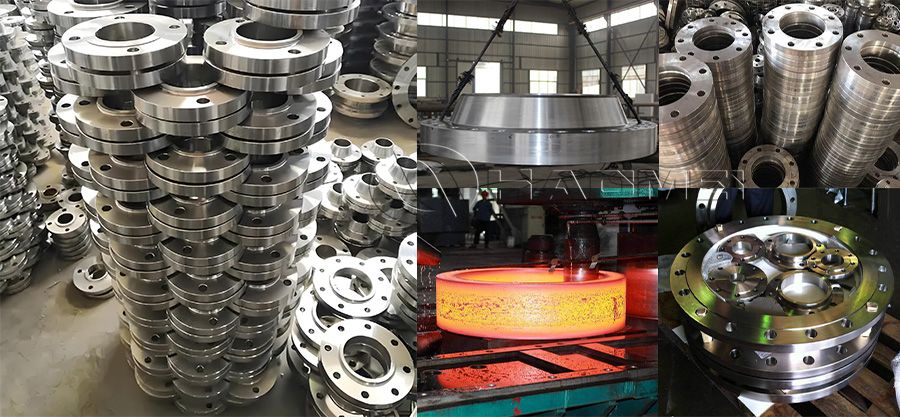
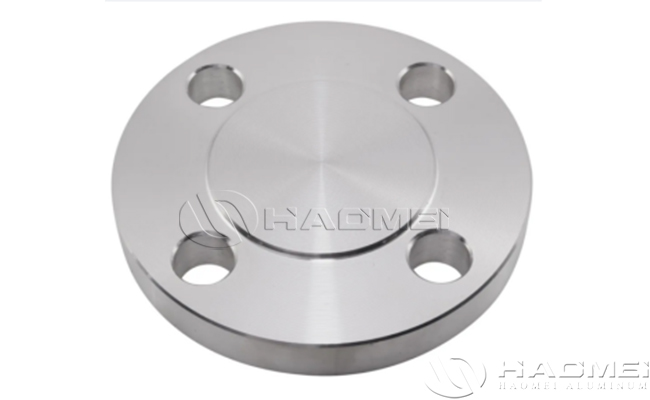
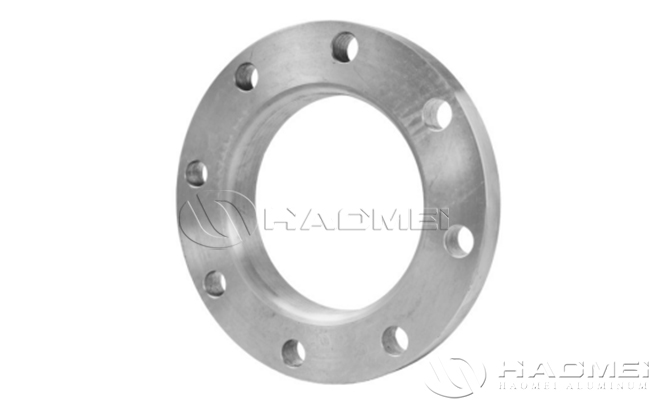
Aluminium Flanges
- Flange Type SO,BL, PL,WN,TH,SW,LJ
- Material 1000-7000 Series
- Size Range 1/2''-24''
- Class 150LBS-2500LBS, PN6-PN40
- Surface Treatment Anodized
- Introduction
- Feature
- Application
- Pictures
- Video
- Download
What Are Aluminum Flanges?
Aluminum flanges are aluminum flanged fittings that are typically used at the end of a pipe to connect to a valve, pump, meter or other device. They can provide a removable interface and are capable of withstanding high pressures and temperatures. Aluminum flanges are usually made of aluminum alloy and are characterized by light weight, corrosion resistance and relatively low cost. These styles include slip on, weld neck, socket weld, blind, screwed, and plate type.

Aluminum Flanges Product Specification:
Aluminium Flanges | Flange Type | SO,BL, PL,WN,TH,SW,LJ |
Material | 1000-7000 Series | |
Size Range | 1/2''NB -24'' NB | |
Dimensions | ANSI/ASME B16.5, B 16.47 Series A & B, B16.48, BS4504, BS 10, EN-1092, DIN, etc | |
Class | 150#, 300#, 600#, 900#, 1500#, 2500#, PN6, PN10, PN16, PN25, PN40, PN64, PN100, PN160 etc. | |
Surface Treatment | Anodized | |
Standard | ANSI B16.5, ANSI B16.47, DIN2576, DIN2502, DIN2527,JIS |
Types of Aluminum Flanges:
Product | Size |
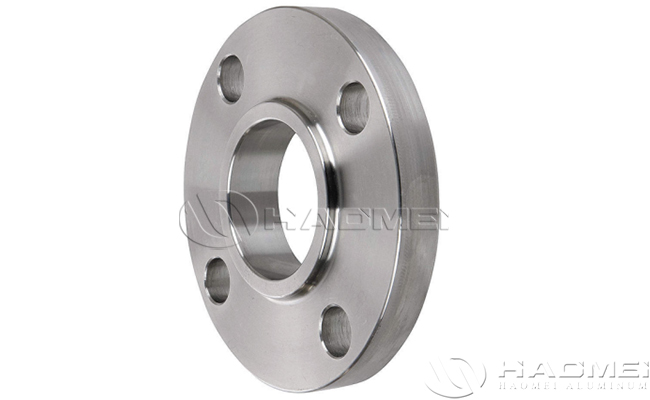
Aluminium Slip On Flanges | 1/8″ – 36″ |
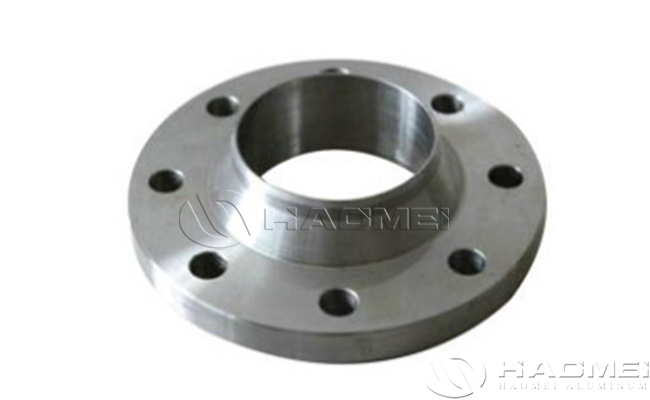
Aluminium Weld Neck Flanges | |
Aluminium Blind Flanges | |
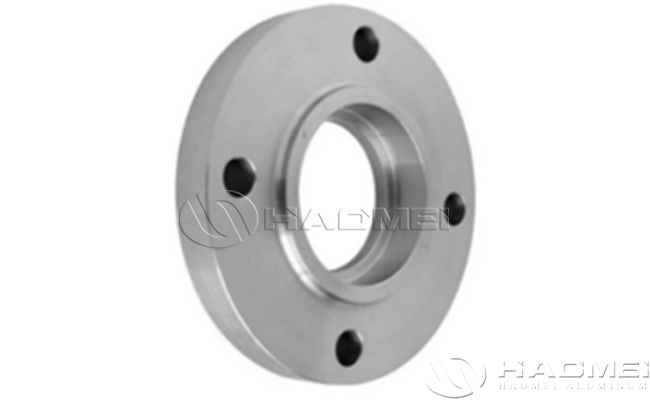
Aluminium Socket Weld Flanges | |
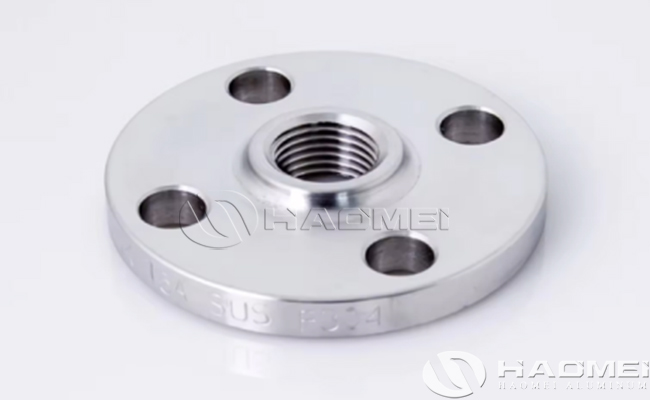
Aluminium Threaded Flanges | |
Aluminium Plate Flanges | |
Aluminium Long Weld Neck Flanges | |
Aluminium Reducing Flanges | |
Aluminium Forged Flanges | |
Aluminium Lap Joint Flanges | |
Aluminium ANSI B16.5 Flange | |
Aluminium ASTM Flanges |
Classification by connection method
Type | Structural Characteristics | Applicable Scenarios |
Slip On Flange | The inner diameter of the flange ring is slightly larger than the outer diameter of the pipeline, and is connected to the outer wall of the pipeline through the fillet weld. | Low-pressure, normal-temperature systems (e.g., water supply, ventilation piping), low cost, easy to install. |
Weld Neck Flange | With tapered neck, butt welding with pipeline, high strength of weld and uniform stress distribution. | High-pressure, high-temperature or severe vibration pipelines (such as chemical and energy systems). |
Threaded Flange | The inner hole of the flange is threaded and screwed to the outer thread of the pipe without welding. | Small low-pressure piping (such as instrumentation piping), the need for frequent dismantling of the scene. |
Socket Weld Flanges | The flange bore has a groove (socket) and is connected to the pipe by socket welding. | Chemical and pharmaceutical industries, lightweighting requirements, cryogenic and heat dissipation systems. |
Blind Flange | No center hole, used to close the end of the pipe or isolate the system. | System pressure test, equipment maintenance isolation (such as reactor manhole cover). |
Classification by sealing surface type
Type | Sealing surface structure | Features and Applications |
Flat Flange (FF) | The sealing surface is flat and glossy and requires a soft gasket (rubber, PTFE). | Low pressure normal temperature water/gas system (PN≤1.6MPa), low cost. |
Raised Face Flange (RF) | The sealing surface has a ring-shaped projection, and with the concave gasket to increase the sealing pressure. | Medium and high pressure system (PN1.6~10.0MPa), the most versatile (such as petrochemical pipeline). |
Concave Face Flange (MFM) | A pair of flanges with flanges and grooves respectively, gaskets embedded in the grooves, sealing more reliable. | High pressure, easy to leak the medium (such as liquefied gas, toxic fluids), need to be strictly sealed occasions. |
Tongue and groove face flange (TG) | One flange with tongue and groove, the other with groove, metal gasket stuck into the groove, excellent sealing. | Ultra-high pressure, high temperature or strong corrosive media (such as hydrofluoric acid pipeline), nuclear industry and other special areas. |
Ring Joint Face (RJ) | The sealing surface is an annular metal groove with an oval metal ring gasket, which is sealed by bolt compression and deformation. | High-pressure, high-temperature oil and gas system (such as API standard oil pipeline), pressure capacity up to PN25.0MPa or more. |
Aluminum Pipe Caps Production Process:
The manufacturing process of aluminum flange usually includes the following steps:
- Material selection: firstly, choose suitable aluminum alloy materials, commonly used aluminum alloys are 6061, 6063, etc. These alloys have good mechanical properties and corrosion resistance.
- Cutting: The aluminum alloy material is cut into the required size and shape, usually using techniques such as laser cutting, plasma cutting or waterjet cutting.
- Forming: The cut aluminum material is formed by casting, forging or machining. Casting flanges are usually formed by melting the aluminum alloy and pouring it into a mold, while forging flanges are forged to increase the strength of the material.
- Machining: After molding, the flanges need to undergo further machining, such as drilling, milling and turning, to ensure that the flanges' dimensions, flatness and hole accuracy meet the design requirements.
- Surface treatment: In order to improve the corrosion resistance and aesthetics of aluminum flanges, they are usually anodized, painted or given other surface treatments.
- Inspection and testing: Finally, the finished products are subjected to quality inspection, including tests on dimensions, appearance and mechanical properties to ensure that they meet the standards.
Aluminium Flanges Core Advantages:
- Lightweight: With its lower density, aluminum flanges are lighter than steel flanges, making them suitable for applications with stringent weight requirements.
- Corrosion resistance: Aluminum has good corrosion resistance, especially in certain chemical environments, which is more advantageous than steel.
- Good Thermal Conductivity: Aluminum has better thermal conductivity and is suitable for applications that require rapid heat dissipation.
- Ease of machining: Aluminum is easy to machine and can achieve complex shapes and high precision design requirements.
- Aesthetics: Aluminum flanges have a smooth appearance after surface treatment and have a better visual effect, making them suitable for applications that require appearance.
- Cost-effectiveness: Although the unit price of aluminum may be higher than that of some steel materials, it may reduce maintenance and replacement costs in long-term use due to its light weight and corrosion resistance.
Applications of Aluminum Flanges:
- Water treatment and chemical industries: aluminum flanges are used in these industries to connect various pipes and equipment to handle liquids and gases.
- Refrigeration and air conditioning systems: aluminum flanges are used in this field to connect components such as compressors, condensers, evaporators, etc.
- Industrial Production Lines: In automated production lines, aluminum flanges are used to connect pipes of different equipment to transport materials or perform other operations.
- Automotive Manufacturing: In automotive manufacturing, aluminum flanges are used for engine cooling systems, turbocharging systems, etc.
- Construction Engineering: In building water supply and drainage and fire fighting systems, aluminum flanges are used to connect large pipes.